| |
|
1. Obtain one dose of injectable, needle and syringe
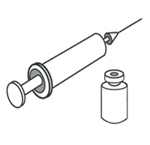 |
- DMPA: 150 mg for injections into the muscle (intramuscular injection). NET-EN: 200 mg for injections into the muscle.
- If possible, use single-dose vials. Check expiration date. If using an open multidose vial, check that the vial is not leaking.
- DMPA: A 2 ml syringe and a 21–23 gauge intramuscular needle.
- NET-EN: A 2 or 5 ml syringe and a 19-gauge intramuscular needle. A narrower needle
(21–23 gauge) also can be used.
- For each injection use a disposable auto-disable syringe and needle from a new, sealed package (within expiration date and not damaged), if available.
|
| 2. Wash |
- Wash hands with soap and water, if possible.
- If injection site is dirty, wash it with soap and water.
- No need to wipe site with antiseptic.
|
| 3. Prepare vial |
- DMPA: Gently shake the vial.
- NET-EN: Shaking the vial is not necessary.
- No need to wipe top of vial with antiseptic.
- If vial is cold, warm to skin temperature before giving the injection.
|
| 4. Fill syringe |
- Pierce top of vial with sterile needle and fill syringe with proper dose.
|
| 5. Inject formula |
- Insert sterile needle deep into the hip (ventrogluteal muscle), the upper arm (deltoid muscle), or the buttocks (gluteal muscle, upper outer portion), whichever the woman prefers. Inject the contents of the syringe.
- Do not massage injection site.
|
|
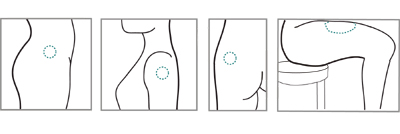
|
6. Dispose of disposable syringes and needles safely
 |
- Do not recap, bend, or break needles before disposal.
- Place in a puncture-proof sharps container.
- Do not reuse disposable syringes and needles. They are meant to be destroyed after a single use. Because of their shape, they are very difficult to disinfect. Therefore, reuse might transmit diseases such as HIV and hepatitis.
- If reusable syringe and needle are used, they must be sterilized again after each use (see Infection Prevention in the Clinic).
|