Chapter 18 Download Chapter
Explaining How to Use Symptoms-Based Methods
TwoDay Method
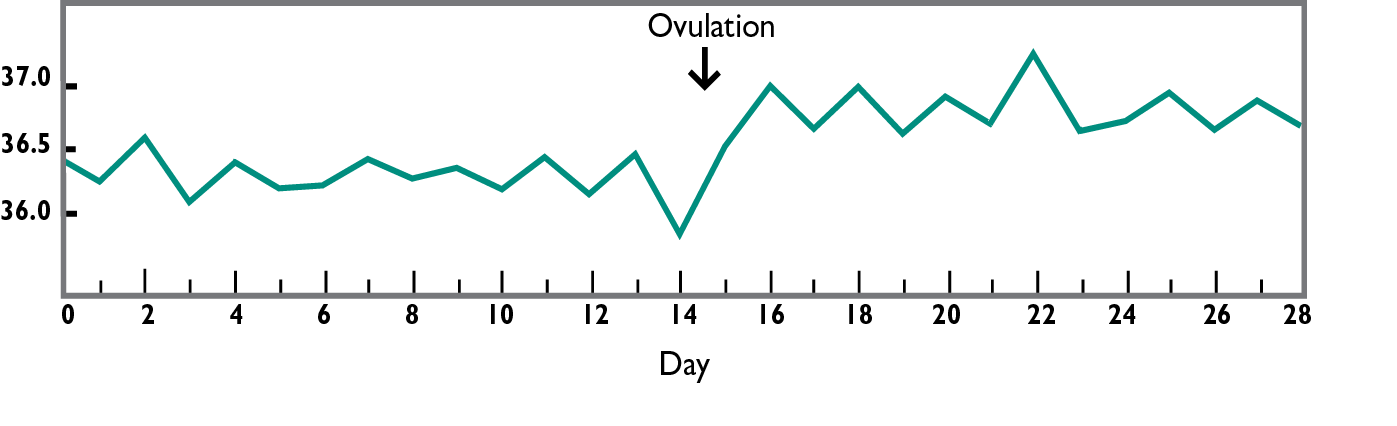
Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Method
|
IMPORTANT: If a woman has a fever or other changes in body temperature, the BBT method will be difficult to use. |
|
| Take body temperature daily |
|
| Avoid sex or use another method until 3 days after the temperature rise |
|
| Resume unprotected sex until next monthly bleeding begins |
|
|
|
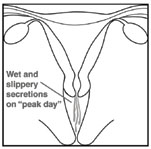
Ovulation Method
|
IMPORTANT: If a woman has a vaginal infection or another condition that changes cervical mucus, this method may be difficult to use. |
|
| Check cervical secretions daily |
|
| Avoid unprotected sex on days of heavy monthly bleeding |
|
| Resume unprotected sex until secretions begin |
|
| Avoid unprotected sex when secretions begin and until 4 days after "peak day" |
|
| Resume unprotected sex |
|